Publisher
India Pharma Outlook
published at
June 20, 2025
Small Pharma Units Face Closure Over Schedule M Non-Compliance — What Can Be Done?
A guide for MSMEs and pharma project partners to avoid shutdowns with GMP-compliant upgrades
India’s small pharma units are in crisis.
As of May 2025, only 1,700 out of an estimated 6,000 MSME drug manufacturers submitted upgrade plans under the revised Schedule M GMP norms.
That means over two-thirds of small manufacturers failed to take the necessary steps toward compliance, exposing them to license cancellation, production shutdowns, and permanent market exclusion.
This isn’t just a regulatory issue. It threatens widespread disruption across the pharmaceutical supply chain, including drug shortages, job losses, and increased healthcare costs.
What went wrong — and what can be done to avoid a worst-case scenario?
Why MSMEs Are Struggling With Schedule M Compliance
The gap between regulation and reality stems from stringent new Schedule M requirements that many small pharmaceutical manufacturers have struggled to meet. In late 2023, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare revised Schedule M guidelines, significantly elevating India’s GMP standards to align with WHO-GMP and global best practices. These updated guidelines now explicitly cover the design, infrastructure, and operational practices of pharmaceutical manufacturing plants.
Key Mandated Upgrades Under the Revised Schedule M
To align with the 2023 revision of Schedule M, pharmaceutical manufacturers must implement comprehensive upgrades across five critical domains. These changes reflect a shift toward global Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) alignment, mirroring World Health Organisation (WHO)- GMP and international audit expectations.
Below is a simplified breakdown of the mandatory upgrade areas and what each involves:
1. Quality Systems & Risk Management
- Implement a comprehensive Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) with top-level accountability and oversight.
- Integrate formal Quality Risk Management (QRM) into operations
- Conduct Annual Product Quality Reviews (PQRs) covering deviations, CAPAs, complaints, and equipment qualification (e.g., HVAC, purified water, gases)
2. Facility & Equipment Standards
- Ensure facilities are used exclusively for drug manufacturing
- Install and qualify cleanrooms, HVAC systems, and purified water units
- Design layouts with segregated zones (e.g., weighing, QA) and controlled personnel/material flows to prevent cross-contamination
3. Documentation, Change Control & Oversight
- Maintain detailed process documentation with audit trails to ensure data integrity
- Apply formal change control protocols classified by risk for any updates to methods, equipment, or software
- Establish mandatory escalation procedures and recall systems for serious quality issues
4. Quality Control & Validation
- Validate cleaning procedures, stability testing, and defined product hold times
- Conduct regular supplier audits
- Perform IQ/OQ/PQ validation for all GMP-impacting computerised systems, and implement backup systems
5. Workforce Training & Hygiene Standards
- Provide regular GMP training and competency assessments for all personnel
- Maintain updated training records
- Enforce strict hygiene protocols, define roles (e.g., Production and QC Heads), and implement visitor access controls
Why Are MSME Pharma Companies Struggling to Meet GMP Standards?
The following operational and systemic challenges have prevented many MSME manufacturers from meeting compliance requirements:
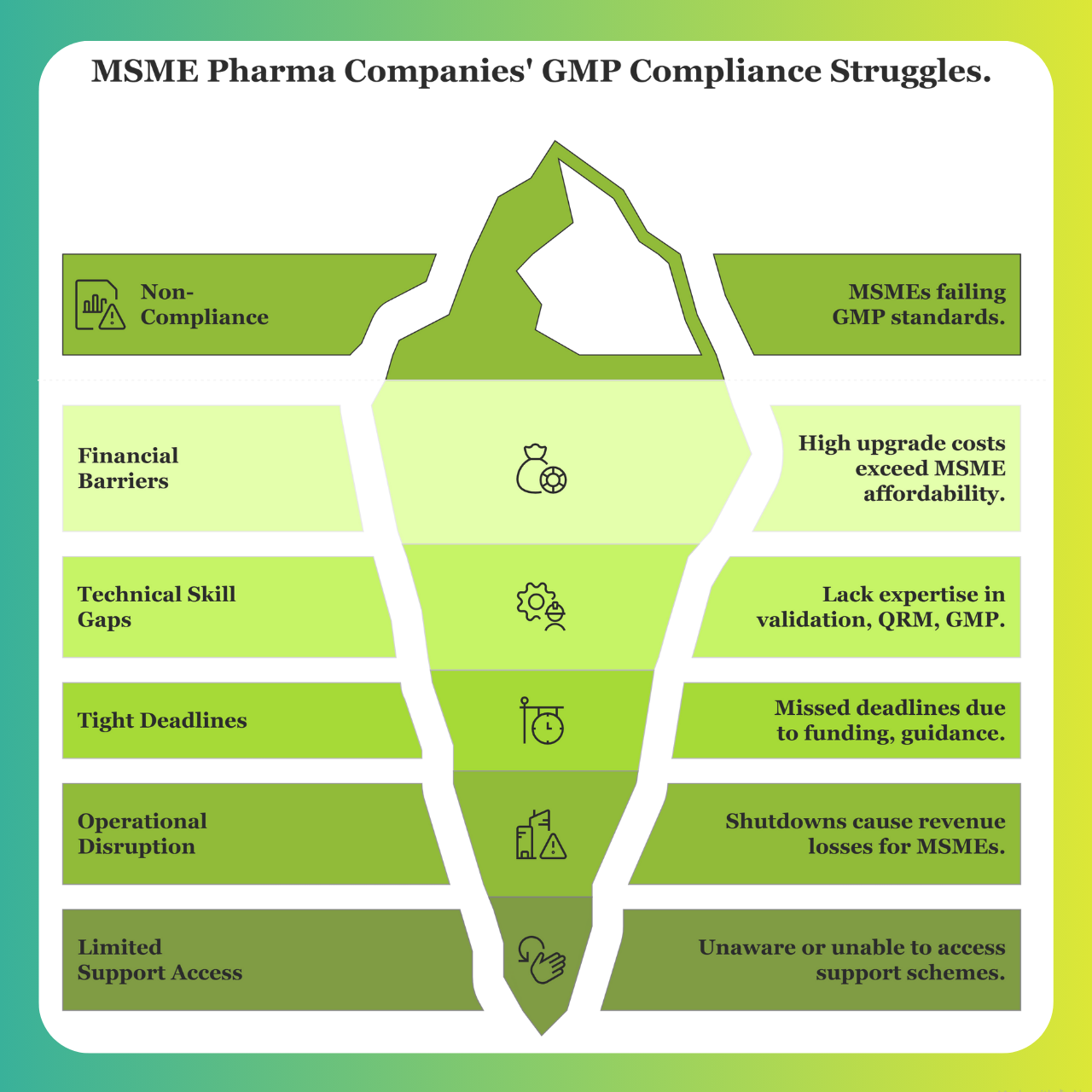
1. Financial Barriers
Implementing upgrades such as HVAC systems, cleanrooms, utility lines, and GMP monitoring tools can cost several crores, a figure well beyond what most MSMEs can afford without external financial support. With already thin operating margins and limited access to institutional capital, both the required investments and potential production downtimes have become insurmountable hurdles.
2. Technical & Skill Gaps
The revised norms require advanced technical expertise in areas such as validation protocols, Quality Risk Management (QRM) frameworks, and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) documentation. Most MSMEs lack in-house capabilities and must rely on external consultants or senior QA personnel, which adds substantial cost and hiring complexity.
3. Tight Compliance Deadlines
The initial deadline for compliance was set for December 2024. However, the government granted a conditional extension to December 2025 — but only to those units that submitted formal upgrade plans by May 2025. Many firms missed this critical milestone, often due to funding limitations or lack of access to regulatory guidance.
4. Operational Disruption Risk
Facility upgrades often require full or partial production shutdowns. For MSMEs, even brief downtime periods can result in significant revenue losses. As a result, many companies deferred upgrades in the hope of further deadline extensions or regulatory leniency, creating a Catch-22 scenario that ultimately led to non-compliance.
5. Limited Access to Support Schemes
While government programs, such as soft loans and subsidies, do exist, including those under the SPI initiative, many MSMEs were either unaware of these schemes or lacked the internal resources and documentation required to apply. Without strong industry networks or guidance from project partners, these companies failed to tap into available assistance.
The Real Impact: Drug Shortages & Job Losses
Non-compliance is not a victimless issue – the fallout from the mass closure of small pharmaceutical units could be significant for public health and the economy. Below is a snapshot of the potential impact if thousands of MSME manufacturers cannot continue operations:
MSME pharma units at risk
- 4,000+ small drug manufacturers facing shutdown (out of ~6,000 targeted for upgrades).
- These are companies that failed to file compliance plans and may be ordered to halt production.
Job losses in the sector
- Thousands of pharmaceutical jobs could be lost as plants close.
- Industry executives warn of severe unemployment; one industry body cautioned that, including indirect employment, “millions” of livelihoods might be affected in a worst-case scenario.
Drug shortages risk
- Essential medicines shortages are a real worry.
- If even a fraction of these units stop production, supplies of certain drugs could dwindle.
- Experts specifically fear shortages in areas such as oncology (cancer medicines), where only a few manufacturers are in operation.
- Other critical or low-cost drugs, primarily manufactured by small firms (such as antibiotics and TB drugs), may also experience gaps in availability.
Market price increases
- Rising drug costs are likely if the supply drops.
- Fewer manufacturers mean less competition; with supply constraints, prices of affected drugs could escalate sharply.
- Patients might face higher out-of-pocket costs, and the overall market could see inflation in certain generic medicine prices due to the disruption.
Why Compliance Is Now a Competitive Advantage
GMP compliance is no longer a checkbox—it’s a survival filter. With India housing over 10,500 drug manufacturing units (8,500+ MSMEs), regulatory upgrades under Schedule M are redrawing the pharma landscape. In high-stakes export markets like those aligned with WHO-GMP, being audit-ready now directly translates to market access.
Early movers are gaining ground—securing contracts, passing inspections, and winning regulator trust. Those who stalled are now firefighting.
Here’s a snapshot of how two MSMEs fared based on when they acted:
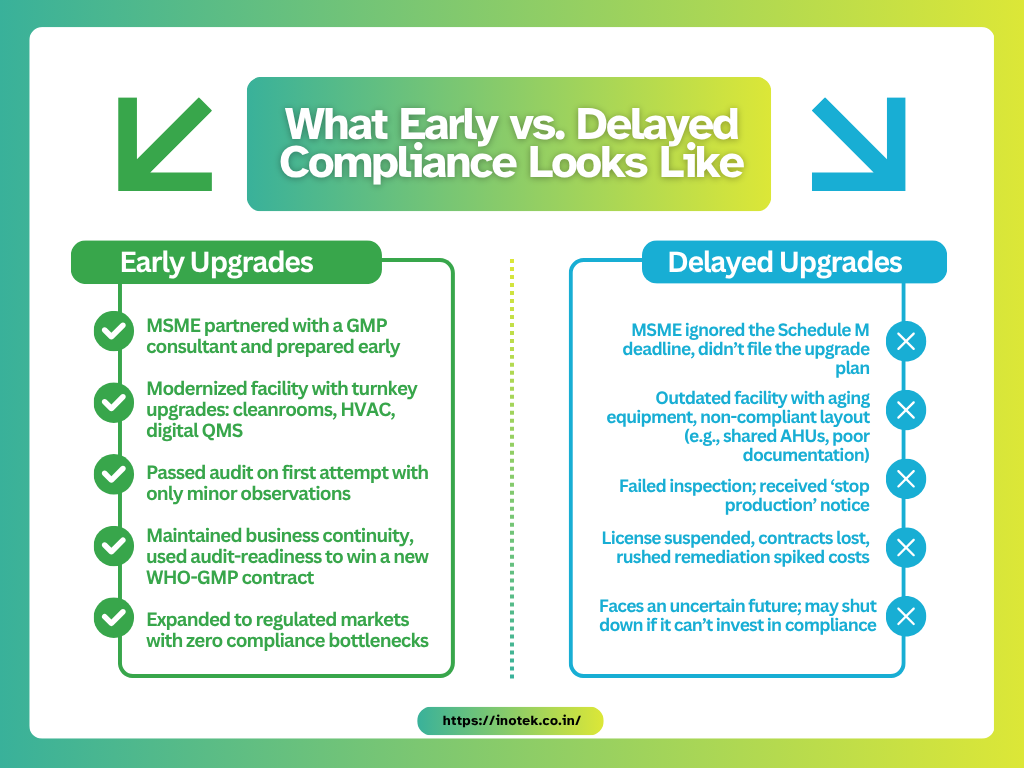
The takeaway : Compliance is no longer overhead—it’s part of your value proposition. Upgrading to global GMP standards reduces audit risk and builds client confidence. Big pharma and procurement agencies prefer suppliers with audit-proof facilities.
Quality compliance is now a genuine market differentiator. Non-compliance means being forced out, whether through shutdowns or lost relevance. In today’s landscape, investing in compliance is investing in competitiveness.
A Clear Path Forward: What MSMEs and Project Partners Can Do
If you're a pharma MSME owner or a project manager supporting one, here’s a concise 5-step roadmap to navigate the Schedule M compliance crunch:
Step 1: Assess Gaps and Plan Upgrades
Begin with a GMP gap analysis to identify areas of non-compliance, such as HVAC systems, facility layout, and documentation practices. Engage QA/QC experts to audit your facility against Schedule M checklists. Utilize their findings to develop a comprehensive upgrade roadmap that outlines facility modifications, equipment requirements, and training needs.
💡 If you haven’t already submitted an upgrade plan, do so immediately. Units that submitted plans by May 2025 received a compliance extension until December 2025.
Prioritise high-risk areas first, and phase upgrades where necessary to avoid complete production shutdowns.
Step 2: Partner with Turnkey Experts
GMP compliance is not just a checklist—it spans engineering design, HVAC, utilities, cleanrooms, and quality systems. A turnkey design partner can integrate all these components under one roof, managing layout planning, equipment selection, installation, and validation.
This approach avoids rework, ensures compliance from day one, and allows your internal teams to focus on ongoing operations while professionals manage the upgrade, from concept to commissioning.
Step 3: Adopt Real-Time GMP Monitoring
Install IoT-enabled sensors and data loggers to continuously monitor key Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and cleanroom pressure. Integrate eQMS tools to digitise document control, CAPA tracking, training logs, and SOP management.
These systems:
- Reduce manual errors
- Ensure continuous compliance (not just for audit day)
- Build defensible, real-time audit trails
Modern monitoring not only protects product quality but also enhances efficiency and regulatory readiness.
Step 4: Build a Quality-Driven Workforce
Technology alone isn’t enough. Your people must own compliance at every level.
- Train all employees on revised SOPs, hygiene protocols, data integrity, and GMP roles.
- Appoint a dedicated validation lead to oversee the ongoing CQV
- Encourage ownership by involving shop-floor teams in solving quality issues
Audit-readiness should become an integral part of your facility's culture, not a one-time event. A trained, invested team will help reduce deviations, improve documentation accuracy, and support long-term GMP performance.
Step 5: Leverage Government Schemes and Phase Investments
Take advantage of financial support under the SPI initiative and PTUAS scheme.
Eligible MSMEs can access:
- Subsidies or loan interest subvention for qualifying upgrades
- Grants for HVAC, labs, purified water systems, and ETPs
Use phased execution to control cost and maintain continuity:
- Retrofit one line while another remains active
- Temporarily outsource specific production steps to avoid shutdown
With proper planning and support, even capital-constrained MSMEs can meet compliance goals. But delays only compound risk.
Useful Government Links for MSMEs
Schedule M: Crisis or Opportunity for MSME Pharma?
The revised Schedule M guidelines mark more than a regulatory shift—they signal a structural turning point for India’s MSME pharma sector. For many, this is the most critical upgrade cycle in decades. Thousands of small and mid-sized pharma companies now stand at a crossroads: invest in compliant infrastructure or risk shutdown and market exclusion.
But amid the pressure lies opportunity. Companies that act with urgency—aligning facility upgrades, CQV timelines, and digital GMP systems—won’t just survive, they’ll grow. Early adopters are already securing audit approvals, export readiness, and global contracts, while others struggle to catch up.
If you’re part of a project, validation, QA/QC, or engineering team supporting MSME pharma, your role is pivotal. Proactive facility planning, turnkey execution, and real-time GMP monitoring will determine who stays in business and who leads it.
Build Once. Pass Every Time. Scale Without Regret.
Need to align your facility with Schedule M, avoid shutdown risk, or prepare for regulatory inspections?
Inotek partners with pharma companies to deliver GMP-compliant, audit-ready facilities—from design and execution to validation and scale-up
Inotek: Your Strategic Partner in GMP-Compliant Facility Upgrades for MSME Pharma
The complexities of Schedule M compliance demand specialised expertise and execution discipline. This is where Inotek steps in as your strategic partner.
We don’t just retrofit pharmaceutical facilities; we engineer audit-ready, regulatory-aligned infrastructure into every project we deliver, fully aligned with the CDSCO, WHO-GMP, and international guidelines, such as those from the EMA and FDA.
Our comprehensive approach includes:
Turnkey GMP Facility Design:
End-to-end architectural and utility layouts built to meet cleanroom zoning, HVAC segregation, and regulatory flow protocols.
HVAC and Utility Requalification:
Systematic assessment and upgrade of HVAC, purified water, steam, and cleanroom controls—delivered with complete IQ/OQ/PQ documentation.
Validation-Led Project Execution:
Design decisions are driven by CQV and audit-readiness goals from day one, ensuring fewer compliance gaps post-handover.
Real-Time GMP Monitoring Systems:
Deployment of IoT-based environmental controls and digital batch/data tracking tools to maintain continuous compliance and enable remote audit support.
By partnering with Inotek, pharma manufacturers have achieved:
- 40% faster facility readiness for audit and licensing
- Significant reduction in CAPA triggers and compliance deviations
- First-time clearance in CDSCO and FDA inspections across upgraded zones
- WHO-GMP certification within 6 months of project completion
Built for Now, Designed for What’s Next
While compliance forms the baseline, future-ready pharma plants must also address growing priorities like:
- Operational scalability and modular expansion
- Environmental sustainability and ESG reporting
- Data integrity and digital QMS integration
At Inotek, we ensure your facility isn’t just compliant—it’s engineered for long-term resilience, efficiency, and regulatory success.
Ready to Retrofit or Expand with Confidence?
Recognised among India’s Top 10 Pharma Turnkey Contractors & Project Consultants in 2022 & 2025, Inotek helps pharma MSMEs upgrade facilities aligned with CDSCO, WHO-GMP, and EMA standards — ensuring you pass audits the first time, every time.
📞 Connect with our experts today or visit www.inotek.co.in to schedule a consultation with Mr. Rohit Ochaney. Whether you're planning a greenfield project or optimising an ageing plant, Inotek ensures your facility is future-proof, compliant, and competitive.
FAQs
What is Schedule M compliance in the pharmaceutical industry?
Schedule M compliance refers to adherence to India’s revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for pharmaceutical manufacturing, including upgraded standards for facility design, HVAC systems, cleanroom layout, documentation, and quality control. The latest 2023 update aligns closely with WHO-GMP, raising the bar for infrastructure, validation, and hygiene protocols.
Why are MSME pharma companies struggling to meet Schedule M deadlines?
Many MSME pharma companies lack the capital, technical resources, and regulatory knowledge to implement Schedule M upgrades. High costs for HVAC, cleanrooms, QMS software, and qualified staff, along with tight timelines and limited access to government schemes, are the main hurdles.
What are the consequences of GMP non-compliance for a drug manufacturer?
GMP non-compliance can lead to license suspension, production halts, loss of export contracts, and reputational damage. It can also lead to drug shortages, particularly for critical therapies such as oncology and antibiotics, and trigger price hikes due to reduced supply.
How can pharma MSMEs upgrade facilities to meet Schedule M norms?
Upgrading to Schedule M-compliant facilities involves a 5-step roadmap:
1. Conduct a GMP gap assessment
2. Engage turnkey pharma consultants
3. Implement phased infrastructure upgrades
4. Adopt real-time GMP monitoring tools
5. Train staff and build a quality culture
What type of support is available for MSMEs to implement Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) upgrades?
MSMEs can access financial support through the Pharmaceutical Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (PTUAS) under India’s SPI initiative. Subsidies, interest subsidies, and technical aid are available for eligible units investing in Schedule M or WHO-GMP compliance upgrades.
How does Inotek help MSME pharma companies avoid shutdowns?
Inotek partners with MSME drug manufacturers to design, upgrade, and validate GMP-compliant pharma facilities. With turnkey solutions spanning HVAC, cleanroom design, QMS integration, and validation documentation, Inotek ensures facilities are audit-ready and compliant, reducing downtime and regulatory risks.
What happens if a drug manufacturing unit shuts down due to GMP non-compliance?
When a pharma unit shuts down due to GMP non-compliance, its products vanish from the market, creating immediate gaps, especially if it supplied essential medicines like antibiotics or cancer drugs. This leaves patients and hospitals facing shortages, with few alternatives available. Other manufacturers may take time to scale up, disrupting treatments. On the business front, employees lose jobs overnight, pushing up local unemployment. The company loses all revenue, and many owners cannot afford to recover. With fewer suppliers, drug prices rise as demand outpaces supply. Shutdowns at MSMEs are already cited as a cause for inflated essential medicine prices nationwide.


