Publisher
India Pharma Outlook
published at
September 24, 2025
The Role of Automation in Enhancing Workplace Safety in Pharma Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical manufacturing is one of the most highly regulated and high-risk industries in the world. Cleanrooms, sterile zones, and biologics production environments require uncompromising attention to safety for workers, patients, and end products. Yet, despite stringent protocols, hazards such as chemical exposure, repetitive strain, and contamination risks remain pressing concerns.
This is where pharmaceutical industry automation plays a transformational role. By reducing human intervention in hazardous tasks, enabling real-time monitoring, and aligning operations with global compliance standards, automation enhances workplace safety while driving productivity.
Why Safety is a Priority in Pharma Manufacturing
Errors in pharmaceutical production can have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond financial losses; they also directly impact human health. Worker exposure to active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) can result in chronic illness or incapacitation (OSHA). Similarly, unsafe handling of biologics or failures in HVAC systems may lead to contamination risks and potentially fatal outcomes (FDA).
Regulatory bodies like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. FDA enforce strict safety guidelines to protect both workers and patients. These frameworks are not optional; they are enforceable standards that reflect the industry's ethical, legal, and reputational imperatives.
To understand how automation addresses these risks, we must first examine the hazards that define pharmaceutical workplaces.
Common Workplace Hazards in Pharma Plants
Pharmaceutical manufacturing environments present a wide range of hazards, including chemical, biological, mechanical, ergonomic, and air quality threats. These risks can result in injuries, contamination, and operational disruptions.
For example, exposure to high-potency APIs (HPAPIs) requires advanced containment facilities to protect operators and prevent cross-contamination. Poor ventilation and air handling also elevate risks, especially in sterile manufacturing environments.
Without intervention, these hazards drive up accident rates, increase costs, and can force plants into costly shutdowns during inspections.
To mitigate these risks, pharma companies turn to established safety and compliance standards.
Safety Standards and Compliance Expectations
Pharma companies must comply with a layered set of safety and quality standards:
- ISO 45001 serves as the global standard for occupational health and safety. Facilities that implement it have seen up to a 25% reduction in workplace injuries and a 20% increase in operational productivity.
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) ensure product safety but also cover environmental control, personnel training, and contamination prevention. Facilities that follow GMP maintain consistent product quality while reducing harm to end users.
- GAMP (Good Automated Manufacturing Practice) governs the validation of automated systems, ensuring they meet safety and compliance requirements throughout their lifecycle.
Meeting these standards once is not enough; continuous compliance requires automated audit trails, environmental monitoring, and digital documentation that regulators can verify instantly.
How Automation Enhances Workplace Safety
Automation’s greatest strength lies in reducing direct human involvement in high-risk tasks, combining both safety and efficiency. From robotic arms in packaging lines to AI-powered predictive monitoring, automation transforms hazardous workflows.
Reducing Manual Handling and Repetitive Tasks
Manual handling like lifting heavy drums, repetitive blister packaging, or mixing potent compounds remains a top contributor to musculoskeletal injuries and on-the-job accidents. Collaborative robots (cobots) are specially designed to work safely alongside human operators, often without physical barriers. They excel in precision filling, packaging, and labeling tasks, minimizing strain injuries and human error in these sensitive processes. For example, deployment of cobots in pharmaceutical packaging has helped remove human hands from contamination-sensitive tasks, enhancing sterility and throughput control.
Example: ABB cobots deployed in sterile packaging facilities reduced human exposure in cleanrooms while increasing throughput consistency.
Real-Time Monitoring & Predictive Maintenance
In the pharma industry, unchecked downtime or hidden risks can cost millions and compromise safety. Traditional manual inspections simply can’t keep up, are prone to human error and have delayed responses. Enter IoT-driven cleanroom monitoring: smart sensors collecting real-time data on air quality, humidity, machine vibrations, and more. Coupled with AI-powered predictive maintenance, these systems can flag anomalies like an unstable HVAC system or a failing mixer bearing well before breakdowns occur. This shift from reactive to proactive safety improves uptime, protects sterility, and safeguards employee health.
Isolating Hazard Zones with Automation
Certain pharma zones like biohazard labs, sterile vaccine areas, or zones handling HPAPIs pose severe contamination and exposure risks. Historically, even with PPE, humans entering these zones faced danger. Automation circumvents that risk using Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), robotic handlers, and remote-controlled systems. These technologies can safely transport materials, load bioreactors, and execute sterilisation routines, keeping human workers out of hazardous environments. This not only elevates operator safety but also protects zone purity and minimizes contamination events.
Automation Technologies Improving Safety in Pharma
Several automation systems directly contribute to worker and product safety in pharma plants:
Cobots and Collaborative Robots
Cobots-lighter, flexible robots designed to work alongside humans feature safety-enhancing elements like force-limiting sensors, rounded frames, and compliant control systems that stop immediately on contact, reducing injury risk while improving throughput. Such ergonomic design is ideal for repetitive tasks in pharmaceuticals, striking a balance between automation and worker safety.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are driverless transporters that navigate predefined routes. They reduce the risk of forklift-related accidents and material mishandling, a common issue in intensive production environments. AGVs also offer a strong return on investment; for example, one study found that installation costs were recouped in just eight months, due to wage savings and reduced incident rates.
AI-Driven Environmental Controls
AI-enabled Building Management Systems (BMS) integrate HVAC, pressure, particulate, and filtration controls. They not only maintain cleanroom conditions but also predictively optimize them, ensuring compliance, energy efficiency, and operational reliability. This real-time responsiveness is critical when even small deviations can compromise safety or sterility.
Machine Vision Systems
Machine vision deploys high-resolution cameras and AI to detect on-the-ground safety issues like spills, contamination, or improper PPE in real time. This proactive layer of hazard detection significantly reduces reliance on manual oversight.
Together, these technologies create a safer operational framework where safety is embedded in the process, not just enforced through vigilance. For pharma companies and contractors alike, this means streamlined compliance, minimized risk, and a foundation for dependable facility management.
Implementation Best Practices for Safe Automation
Simply installing automation equipment doesn’t guarantee safety. True success is rooted in responsible planning, rigorous validation, and **continuous training—**all tailored to the pharmaceutical setting.
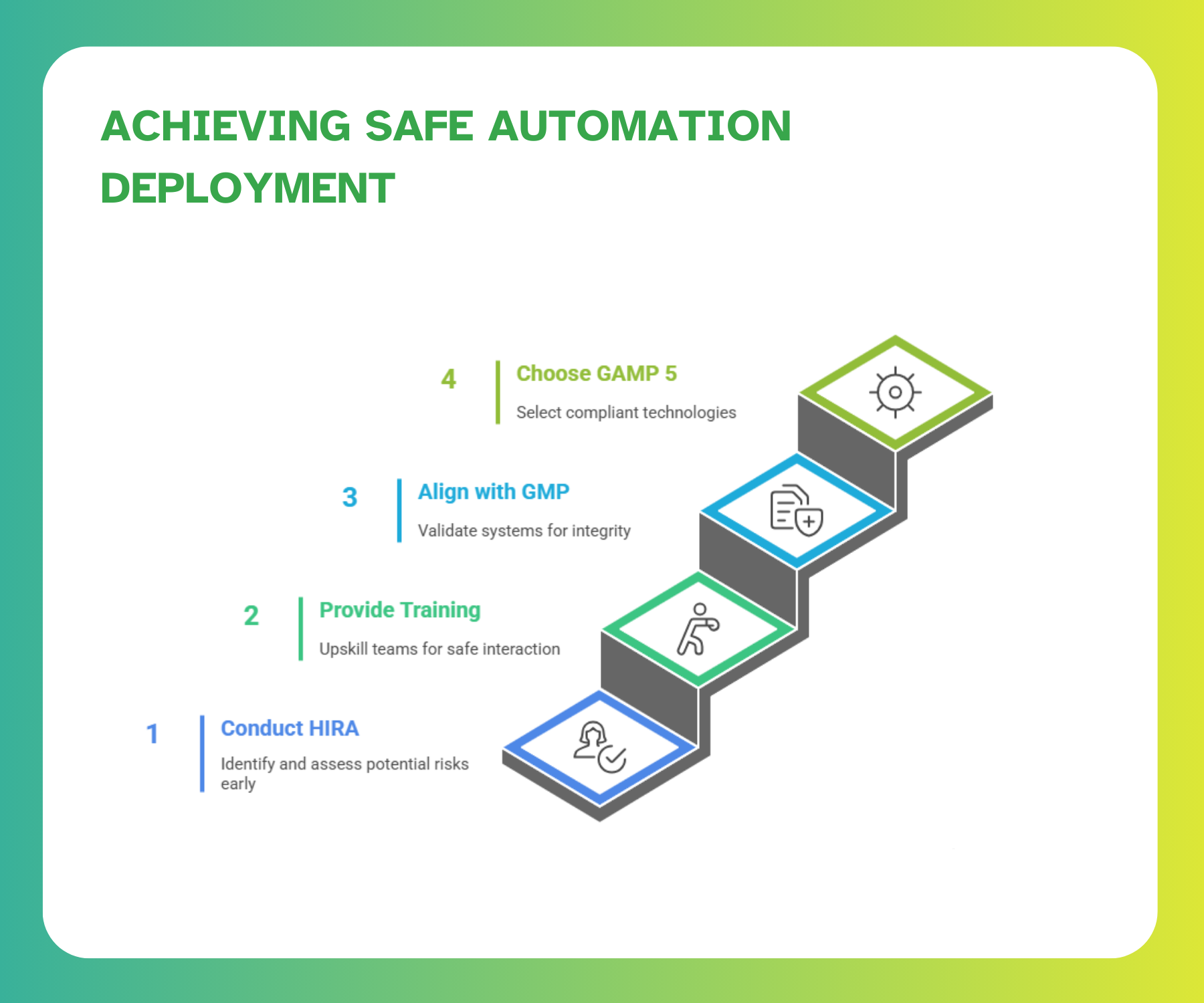
- Safety Assessment Before Deployment
Before deploying any automated system, it's essential to conduct a Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA) to identify potential failure modes or unsafe conditions. HIRA is a structured process that evaluates hazards’ severity, frequency, and likelihood to support informed decisions about technology suitability and protective measures.
This proactive assessment ensures the system is aligned with manufacturing complexities and potential risks are addressed before hitting the production floor.
- Employee Training and Change Management
Automation alters workflows and responsibilities, making targeted employee training indispensable. Traditional “read-and-understand” approaches are no longer sufficient; modern methods must build real skills, ensure long-term retention, and reinforce safe interaction with automated systems.
Strong change management practices create the environment for successful adoption: clear communication, early stakeholder engagement, re-skilling programs, and continuous support to reduce resistance and build workforce confidence.
- Aligning Automation with GMP Compliance
Automated systems must be validated, documented, tested, and traceable to support GMP requirements. Computerized System Validation (CSV) in regulated environments applies a risk-based approach, ensuring that critical and high-risk functionalities receive appropriate validation and documentation. This ensures that the integrity, reliability, and regulatory compliance of automated systems are maintained throughout their lifecycle.
- Choosing the Right Automation Solution
Selecting the right system involves balancing technological fit with compliance and operational needs. The focus should be on systems designed with structured, lifecycle-based validation in mind, following GAMP 5 principles and emphasizing robust documentation and risk management throughout implementation.
This ensures the automation solution integrates seamlessly into pharma operations while supporting safety, regulatory compliance, and future scalability.
Benefits Beyond Safety: Efficiency, Compliance, and ROI
While worker safety is the most important benefit, automation extends far beyond protection. It delivers measurable business value that strengthens both operations and compliance.
Increased Operational Uptime
Predictive monitoring and preventive maintenance reduce unexpected breakdowns. Automated systems detect issues early, allowing timely interventions and ensuring cleanrooms and production lines run smoothly with minimal downtime.
Improved Audit and GMP Compliance
Automation creates accurate, tamper-proof data trails covering environmental conditions, equipment performance, and material flows. This simplifies regulatory audits, reduces reporting errors, and strengthens GMP compliance without adding manual workload.
Long-Term Cost Savings
By lowering accident-related expenses and optimising resource use, automation quickly becomes cost-effective. Consistent precision reduces waste of high-value APIs, while fewer injuries translate into lower insurance and training costs. Over time, these savings deliver a strong return on investment.
Inotek: Your Strategic Partner in Pharma Safety Automation
The complexities of pharmaceutical safety automation demand specialised expertise and compliance-focused execution. This is where Inotek steps in as your strategic partner.
We don’t just integrate machines into facilities; we engineer safety-first, compliant automation systems aligned with global regulatory standards like FDA, EMA, and CDSCO.
Our comprehensive approach includes:
- Cobot & AGV Integration: Minimising human exposure in sterile and high-risk zones while improving throughput efficiency.
- AI-Driven Monitoring Systems: Real-time environmental control and predictive maintenance to safeguard sterility and uptime.
- GMP-Validated Automation: Lifecycle-based validation and documentation aligned with GAMP 5, ensuring regulatory compliance.
- End-to-End Safety Assessments: Hazard analysis and risk management tailored to high-potency APIs and biologics facilities.
By partnering with Inotek, pharma manufacturers have achieved:
- Faster facility commissioning timelines
- Reduced contamination and compliance gaps
- Enhanced workplace safety with measurable ROI
Future-Readiness Beyond Compliance
While compliance forms the foundation, successful automation must also address broader industry priorities such as:
- Digital compliance and data integrity
At Inotek, we ensure your facility isn’t just audit-ready but future-proof and performance-driven.
Recognised among the Top 10 Pharma Turnkey Contractors & Project Consultants in 2022 & 2025, Inotek helps pharma leaders design, build, and automate facilities that meet the strictest GMP and safety standards.
📞 Connect with our experts today or visit www.inotek.co.in to schedule a consultation with Mr Rohit Ochaney.
Whether you’re planning a greenfield facility or optimising an existing setup, Inotek ensures your automation project is safe, compliant, and ready for the future.
FAQs
How does automation improve safety in pharma plants?
By reducing manual handling, limiting chemical exposure, and ensuring continuous monitoring, automation significantly lowers workplace risks.
What types of automation are used in pharma for safety?
Cobots, AGVs, AI-driven monitoring systems, and machine vision are the most commonly used technologies. Each reduces risk in different stages of production.
Can automation help with GMP and audit compliance?
Yes. Automated systems generate traceable logs and validated processes, which regulators favour during audits.
Is automation cost-effective for smaller pharma plants?
Yes. Scalable, modular systems allow smaller plants to adopt automation in phases with clear ROI benefits.
What are the risks of not adopting safety automation?
Companies risk higher injury rates, compliance violations, and reputational damage by delaying automation.




