Publisher
India Pharma Outlook
published at
July 2, 2025
India’s Labelling Upgrade Mandate: Why It Demands a Packaging Expert’s Guidance
In 2025, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) signalled a decisive shift: more apparent, patient-friendly labels, including Braille and QR codes, will no longer be optional. For pharma manufacturers, this means retrofitting packaging lines and revalidating systems under tight timelines. Working with a packaging expert from the outset ensures that critical compliance milestones are identified early and executed without delays.
According to draft guidelines announced by CDSCO in March 2025 and reported by the Economic Times, Notification No. F.1-54/2024-DA outlines proposals for enhanced labelling standards. The public consultation period closed in June 2025. While final enforcement timelines have not yet been published as a Gazette Notification, implementation is anticipated by late 2025, with a transition phase likely extending into 2026. Early preparation remains critical to avoid supply disruptions once the rules are formally adopted.
What Changed in CDSCO Pharma Labelling Guidelines, And Why It Matters
This year, the Drugs Consultative Committee (DCC) under CDSCO established an expert subcommittee, including packaging experts, to overhaul India’s labelling standards. Their remit is clear: address persistent issues such as unreadable expiry dates, small font sizes, and reflective blister foils that compromise patient safety. Engaging a packaging expert provides an additional layer of oversight, ensuring that artwork revisions and tooling validations meet regulatory expectations.
The draft proposals include:
- Mandatory high-contrast printing for expiry, batch, and MRP data
- Standard minimum font sizes across all packs
- Braille inscriptions on mono-cartons to improve accessibility
- Voice-assisted QR codes provide audio instructions
These changes not only align India more closely with EMA standards but also make serialization and traceability a regulatory imperative rather than a best practice.
Impact on Readability, Serialization, and Patient Access
For most companies, these changes are far from cosmetic. Improving readability will require retooling print processes, revising artwork, and qualifying new packaging materials.
Serialization elevates traceability to a regulatory essential. To comply, companies must ensure Braille artwork is reviewed by qualified packaging experts and embossing tooling is validated for consistent dot height and legibility.
Budget and Supply Chain Implications
For smaller manufacturers and MSMEs, aligning labelling investments with broader Schedule MGMP compliance strategies can help spread costs and minimize disruption. Implementing India’s 2025 labelling requirements will bring significant cost and operational impacts. Companies should prepare for:
- Capital Expenditure Increases: Retrofitting packaging lines with Braille embossers, vision cameras, and serialization printers typically raises capital costs by 15–25%.
- Extended Timelines: Procurement and integration can take 12–24 weeks, particularly for specialized modules.
- Supplier Collaboration: Early engagement with packaging vendors and serialization platform providers is essential to align specifications and avoid delays.
- Inventory Management: Transitioning to compliant packaging requires parallel inventories and meticulous planning to prevent obsolete stock.
By anticipating these impacts and building them into project timelines and budgets, manufacturers can avoid last-minute bottlenecks and maintain uninterrupted product availability.
Why an Understanding of Packaging Beyond Basic Compliance is Now Essential
Just as Schedule M establishes essential GMP requirements for facility and process controls, the CDSCO labelling upgrades demand the same level of operational discipline to avoid costly deviations. Superficial fixes, like swapping a font or adjusting a template, will not suffice. Integrating these requirements without disrupting validated processes demands operational depth and a clear understanding of packaging principles.
Consider:
- How do you ensure Braille embossing does not compromise carton integrity?
- What controls prevent duplication or corruption of serialization data?
- How do you maintain print quality consistently across high-speed lines?
Relying on teams with a deep understanding of packaging challenges is critical to avoid costly rework, delays, and compliance gaps.
Change Management and Cross-Functional Coordination
Compliance is not just a packaging issue; it requires coordinated change management across the organisation. A packaging expert can help align the Regulatory Affairs, QA, Engineering, and Procurement functions, ensuring that labeling specifications, validation protocols, and artwork updates are synchronized efficiently.
- Regulatory Affairs: Align updated artwork and labelling specifications with CDSCO submissions.
- Quality Assurance: Revise SOPs and validation protocols to incorporate new inspection and sampling requirements.
- Engineering and IT: Configure hardware interfaces and secure data workflows for serialization.
- Procurement and Supplier Quality: Onboard approved vendors for compliant cartons, foils, and labels.
Without early collaboration and clear ownership, even well-resourced projects risk delays, rework, and compliance gaps.
Why Non-Compliance is High-Risk
Inadequate labelling controls are among the most common findings during Surprise FDA inspections, often triggering observations and corrective actions.
Failing to comply with India’s updated labelling standards is not a minor oversight; it can trigger serious regulatory and commercial consequences. According to CDSCO’s draft enforcement framework, penalties may include:
- Product Recalls: Batches with unreadable expiry dates or non-scannable QR codes can be withdrawn from the market immediately.
- Market Suspensions: Manufacturers risk suspension of product licences until deficiencies are corrected.
- Import or Export Restrictions: Non-compliance can lead to shipments being detained or refused in the EU, US, and other regulated markets.
- Reputational Damage: Public recall notices and regulatory warnings undermine patient trust and partner confidence.
These risks underscore the importance of proactive preparation, robust validation, and specialist guidance in avoiding costly disruptions.
7 Ways Pharma Packaging Lines Must Evolve for CDSCO 2025 Compliance
Pharma manufacturers can no longer rely on minor adjustments to meet updated labelling requirements. Each area of packaging operations will need targeted upgrades to maintain compliance and efficiency.
1. Integration of Voice-Assisted QR Codes
Voice-enabled QR codes are more than an optional upgrade. They represent a shift toward digitally inclusive labelling that improves patient access to critical information. India has already begun enforcing serialization via the Schedule H2 mandate, requiring QR codes on the top 300 selling drug brands. For many manufacturers, this has meant retrofitting printers, integrating vision systems, and validating data flows between ERP systems and packaging lines.
The new proposals go further by encouraging voice-assisted QR codes that deliver expiry and dosage instructions audibly. Implementing this capability requires not only hardware upgrades but also robust data validation processes, secure storage, and clear operator workflows to handle rejects and reprints effectively.
2. Revalidation of Vision Systems and Labellers
Any modification to label artwork, print processes, or inspection equipment will trigger revalidation. Operational Qualification (OQ) protocols must be updated to confirm that labels meet the new standards.
Teams should:
- Test expiry date readability under various lighting conditions
- Confirm QR code scannability across the full product range
3. Potential Need for Braille Embossers
Embossing Braille onto mono-cartons or outer packaging introduces additional controls. Manufacturers must decide whether to install inline embossing modules or integrate pre-embossed materials into the supply chain. In both cases, processes must include:
- Tooling precision
- Dot height verification
- Routine calibration
4. Updates to URS and Functional Specifications
User Requirement Specifications (URS) and Functional Specifications (FS) will require updates to reflect expanded capabilities. These documents should specify:
- Minimum font size and contrast requirements
- Braille embossing tolerances
- 2D barcode data handling and serialization interfaces
Delaying these updates increases the risk of rework downstream.
5. New PQ Protocols for Labelling Modules
Performance Qualification (PQ) will need to confirm that upgraded systems deliver consistent output. Validation must cover:
- 100% readable codes validated across batches
- Braille legibility checks by qualified personnel or third-party validators
- Print durability testing, including smudge and fade resistance
6. Packaging Material Selection and Automation
Upgrading labelling capabilities goes beyond installing new equipment. The choice of packaging substrates and the level of automation have a significant impact on compliance and long-term efficiency.
Material Selection
High-gloss foils and reflective laminates can compromise readability and scannability. CDSCO guidelines recommend matte varnishes, low-reflective inks, and high-opacity coatings to maintain consistent contrast. All materials must be validated to withstand transport stresses and remain legible over the product’s shelf life.
Automation and Inspection Systems
Modern high-speed lines increasingly rely on inline vision systems to verify print quality, serialization codes, and Braille embossing. These technologies capture digital images, flag nonconformities in real-time, and generate audit-ready records.
Operational Efficiency Gains
Although upfront investments are significant, automation delivers clear benefits:
- Reduced manual inspection effort
- Faster line clearance times
- Fewer compliance deviations during audits
Evaluating material upgrades and automation options early ensures packaging lines stay compliant and future-ready.
7. Training Operators on Upgraded Systems
Operators will need to have updated standard operating procedures (SOPs) to maintain compliance and quality. Training programs should include:
- Printer calibration and maintenance
- Braille inspection and sampling procedures
- Troubleshooting serialization rejects and scanning errors
Validation and Documentation for Pharma Labelling Compliance in India
Every change to labelling processes, from QR code integration to Braille embossing, triggers a cascade of validation and documentation requirements. Teams who underestimate the scope of revalidation often lack the necessary understanding of packaging systems and processes, which increases the risk of non-compliance.
Key Validation and Documentation Priorities
To maintain compliance, companies should:
- Revise Performance Qualification (PQ) protocols to confirm readability and scannability across production lots.
- Update Operational Qualification (OQ) scripts for new print heads, cameras, and emboss units.
- Revalidate software generating and storing serialization data to ensure audit trails and compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 for exports.
- Document all changes through formal change controls and updated SOPs.
- Train operators on Braille inspection, QR calibration, and serialization reject management.
Examples of Required Records and Audit Readiness Tips
Maintain a structured library of documentation, including:
- Updated User Requirement Specifications (URS): font size, contrast requirements, Braille tolerances, and serialization handling.
- Functional Specifications (FS): hardware configurations, vision system integration, print durability criteria.
- Validation Protocols: IQ, OQ, and PQ reports validating performance across batches.
- Training Records: operator sign-offs and competency assessments for inspection processes.
Audit Readiness Best Practices:
- Keep a dedicated compliance binder or digital folder with samples labelled 'before' and 'after'.
- Conduct periodic mock inspections to verify that documentation and training logs are complete.
- Assign a single point of contact to oversee updates and version control.
By maintaining clear records and proactive ownership, manufacturers can demonstrate readiness and avoid costly gaps under regulatory scrutiny.
Global Export Compliance: Comparing India’s Rules with FDA & EMA
Pharma manufacturers preparing for India’s 2025 labelling requirements must also align with international regulations. The table below summarises key similarities and differences across CDSCO, EMA, and FDA expectations:
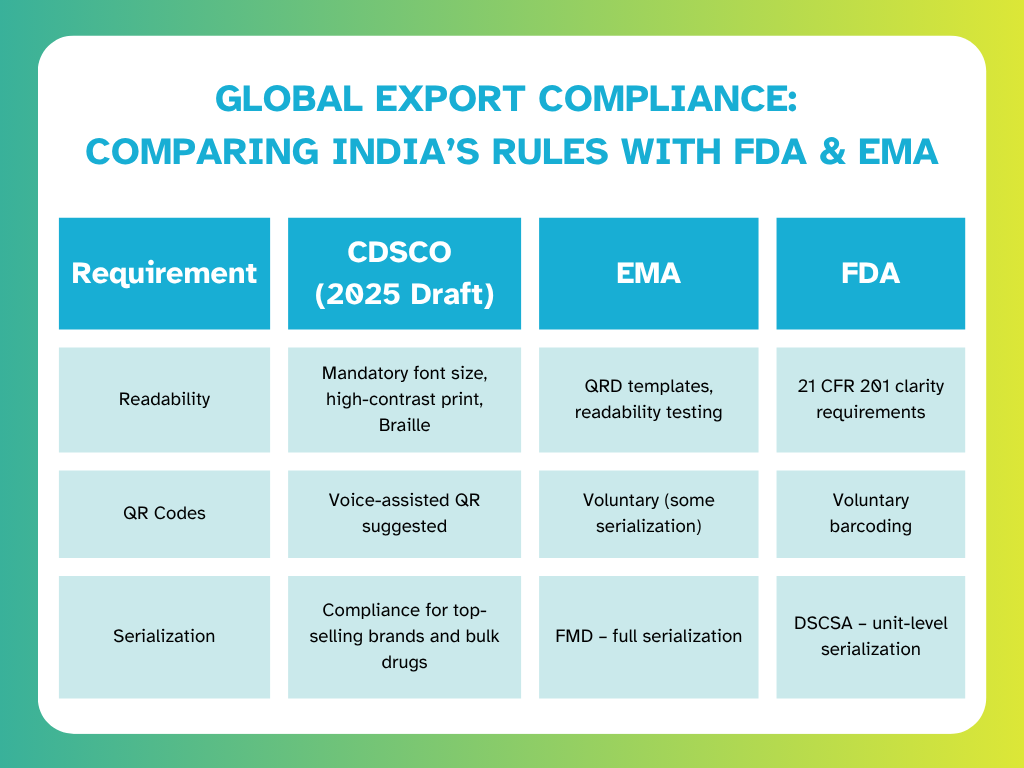
India’s evolving requirements are converging with EU standards for readability and serialization, while still trailing the US DSCSA in supply chain aggregation. For companies exporting globally, it is essential to design packaging configurations that address overlapping obligations without creating redundant SKUs.
EU regulations also mandate tamper-evident features and Braille in the official languages of the destination market. While FDA requirements primarily focus on clarity under 21 CFR 201, many exporters adopt voluntary tamper-evidence and serialization to align with international expectations.
Tip for Regulatory and QA Teams:
When developing global labelling strategies, QA teams should consider creating a single carton architecture that includes:
- Standardised 2D barcodes and tamper-evident features
- Braille is validated in multiple languages
- Flexible zones for country-specific text and symbols
This approach simplifies validation, reduces the number of SKUs, and minimizes supply chain complexity across regulated markets.
CQV Planning for New Projects
Building compliance into new projects is essential to avoid costly retrofits later. For CQV teams, this means:
- Updating User Requirement Specifications (URS) to cover Braille, serialization, and voice-assisted QR capabilities
- Aligning project timelines with enforcement milestones
- Coordinating engineering, IT, and QA to validate hardware, software, and data flows
- Budgeting for equipment, training, and requalification
- Documenting each step to demonstrate readiness during inspections
Digital Validation Tools and Risk Mitigation
As labelling requirements grow more complex, traditional paper-based validation often struggles to keep pace. Digital platforms, such as electronic batch records and cloud-based serialisation systems, enable the capture of real-time data, streamline approvals, and provide reliable audit trails.
To mitigate risk and maintain project momentum, teams should:
- Use FMEA to identify and prioritize hazards linked to labelling upgrades
- Run parallel qualification of new and legacy systems to reduce disruption
- Pre-qualify backup suppliers to avoid supply interruptions
- Track progress using clear dashboards and readiness milestones
Leveraging digital validation and disciplined risk management helps accelerate CQV timelines and maintain compliance across all packaging lines.
Readiness Checklist: Are You Prepared?
Different teams across your organisation play a critical role in ensuring labelling compliance. Use this workflow to confirm whether your operations are ready for upcoming regulatory changes.
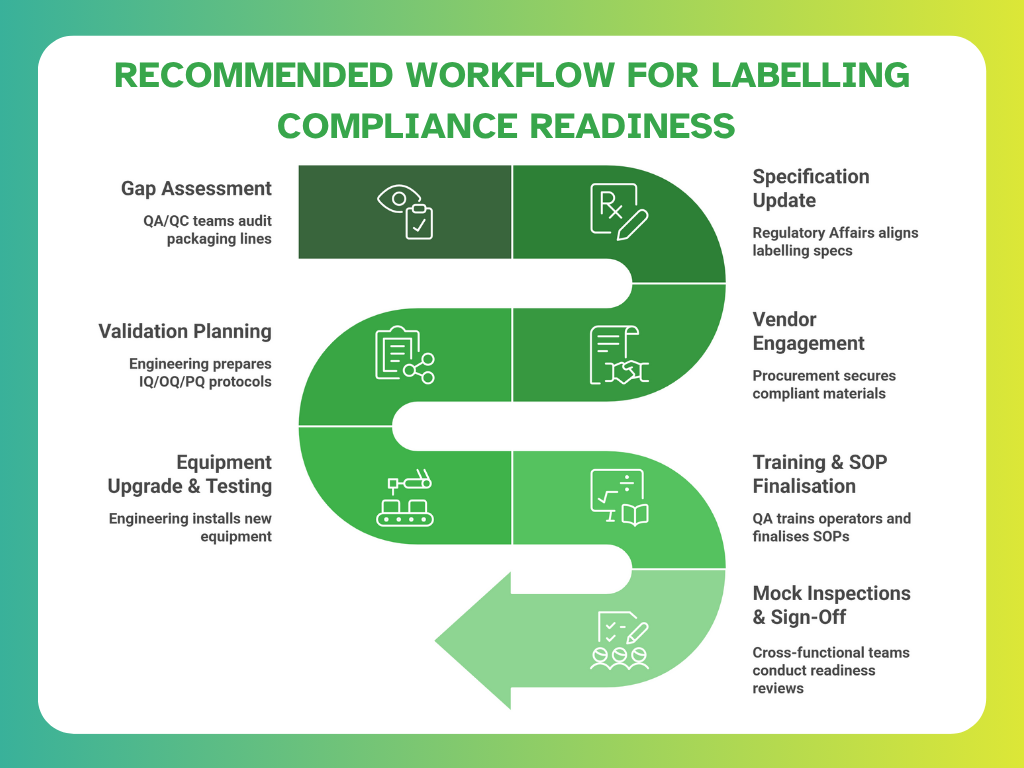
By following this structured approach and assigning clear ownership, manufacturers can avoid last-minute gaps and demonstrate proactive compliance during inspections.
ROI and Efficiency Gains, The Long-Term Value of Compliance
While the immediate focus is regulatory adherence, upgrading labelling and serialization capabilities unlocks tangible long-term benefits:
Faster Line Clearance:
Digital inspection systems and automated reject handling reduce line clearance times by 20–30%, enabling quicker batch turnaround and improved Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
Reduced Recall Risk:
Proactive validation of Braille, QR codes, and high-contrast print quality significantly reduces the likelihood of costly recalls due to mislabeling or traceability failures.
Enhanced Brand Reputation:
Consistent, patient-centric labelling improves user confidence, especially in chronic therapies where clear instructions and legibility are essential.
Operational Visibility:
Integration of serialization and vision systems provides real-time insights into packaging line performance, creating opportunities for continuous improvement.
In a competitive market, these benefits often justify investment far beyond compliance obligations.
Future Trends in Pharma Labelling and Serialization
Emerging technologies are poised to redefine how companies approach packaging compliance and patient engagement:
Digital Twins for Packaging Lines
Virtual replicas of packaging lines allow teams to simulate process changes, predict performance impacts, and test validation scenarios before deployment. Early adopters are utilising digital twins to expedite line commissioning and minimize startup deviations.
💡 McKinsey research highlights digital twins and Pharma 4.0 as critical enablers of packaging modernization, driving faster validation and reducing downtime.
Blockchain Integration
Blockchain technology is being explored as a secure platform for storing and sharing serialization and traceability data across supply chain stakeholders. Immutable audit trails strengthen anti-counterfeiting measures and simplify regulatory reporting.
AI-Enabled Vision Systems
Advanced machine learning algorithms are enhancing defect detection accuracy, particularly for complex variable data, such as Braille and QR codes. Forward-looking companies are already piloting these technologies to future-proof their packaging operations.
💡 Deloitte reports indicate that retrofitting serialization infrastructure can frustrate users and impact costs; nearly half of the survey respondents cited budget constraints and slowed digitalization efforts.
Regulatory Outlook, What’s Next for India?
As CDSCO finalizes labelling requirements in 2025, additional reforms are under consideration:
Aggregation Requirements:
Industry working groups have proposed phased adoption of US DSCSA-style aggregation, where cartons and shipper cases are digitally linked to simplify downstream traceability.
Mandatory Tamper-Evidence:
Following EU precedent, India may soon mandate tamper-evident features for all prescription medicines to strengthen patient safety.
Electronic Leaflets:
Regulators are exploring frameworks for electronic product information (ePI) accessed via QR codes, which could potentially reduce the complexity of printed leaflets.
If your organisation relies on India as a manufacturing hub, staying ahead of these trends will be critical to maintaining supply chain agility and global market access.
Building a Future-Ready Labelling Strategy
India’s 2025 labelling reforms mark a pivotal moment for pharma manufacturers. What began as a drive for clearer, safer packaging has evolved into a complex compliance journey that encompasses every facet of operations, from artwork to automation. Partnering with a trusted packaging expert helps bridge the gap between regulatory requirements and practical implementation. Organisations with an in-depth understanding of packaging will be better prepared to adapt to evolving standards and leverage these changes for competitive advantage.
Organisations that act early can not only mitigate compliance risks but also unlock substantial efficiency gains and position themselves as leaders in patient-centric labelling.
If you’re planning a packaging retrofit or evaluating how these mandates impact your operations, working with a specialist partner is the fastest way to move from uncertainty to confidence.
Planning a labelling upgrade or serialization project?
Connect with Inotek today to access our Labelling Compliance Readiness Blueprint and ensure your packaging lines are globally compliant, efficient, and audit-ready.
Inotek: Your Strategic Partner in CDSCO-Compliant Pharma Labelling and Packaging Upgrades
The complexities of CDSCO 2025 labelling compliance demand specialised expertise and precision-focused execution. This is where Inotek steps in as your strategic partner.
We don’t just retrofit packaging lines; we engineer fully validated labelling and serialisation solutions into every facility we deliver, aligned with global regulatory standards such as the FDA, EMA, and CDSCO.
Our comprehensive approach includes:
Packaging Line Retrofit Design: Engineering Braille embossers, vision systems, and serialization hardware to meet India’s evolving labelling requirements
Digital Validation & Documentation: Implementing electronic batch records and 21 CFR Part 11-compliant systems to accelerate qualification and streamline audits
Regulatory Artwork Development: Supporting artwork redesign and readability enhancements that align with CDSCO and export market expectations
Operator Training & Change Management: Delivering tailored SOPs and hands-on training programs to ensure teams can maintain compliance confidently
By partnering with Inotek, pharma manufacturers have achieved:
- Faster packaging line requalification and go-live timelines
- Reduction in labelling-related deviations and CAPAs during inspections
- Improved traceability and patient safety through validated serialization
While compliance forms the foundation, successful labelling upgrades must also address growing industry expectations around:
- Digital traceability and data integrity
- Supply chain agility and risk mitigation
- Patient-centric packaging and accessibility
At Inotek, we ensure your facility isn’t just audit-ready, but engineered for long-term operational excellence.
Recognised among the Top 10 Pharma Turnkey Contractors & Project Consultants in 2022 & 2025, Inotek helps pharma leaders design, build, and upgrade packaging lines that meet the strictest GMP and sustainability standards.
📞 Connect with our experts today or visitwww.inotek.co.in to schedule a consultation with Mr. Rohit Ochaney.
Whether you’re planning a greenfield facility or optimising an existing setup, Inotek ensures your labelling compliance project is compliant, resilient, and future-proof.
FAQs
What are India’s new pharma labelling requirements in 2025?
The CDSCO’s 2025 labelling mandate requires pharma companies to implement high-contrast printing for expiry dates, batch numbers, and MRP; Braille inscriptions on mono-cartons to improve accessibility; minimum font size standards across all packs; and voice-assisted QR codes that deliver audible product information, dosage, and usage instructions.
When will the CDSCO labelling rules be enforced?
The draft guidelines were issued in March 2025, and the public consultation closed in June 2025. Final enforcement timelines are expected by late 2025, with companies likely being given a transition period into 2026 to upgrade their packaging lines, validate new processes, and train their operational teams.
Do all products need Braille labelling?
According to the draft proposal, all mono-carton packaging, particularly that of prescription medicines, must feature Braille inscriptions displaying the product name and strength. This change enhances accessibility for visually impaired patients and also serves as an anti-counterfeiting measure, as Braille embossing is more challenging to replicate convincingly.
What are the penalties for non-compliance?
Companies failing to comply with CDSCO’s labelling rules risk several penalties, including product recalls from the market, temporary or permanent suspension of licenses to sell affected products, import or export restrictions in other regulated markets, substantial financial losses, and damage to the organisation’s brand reputation and patient trust.
How can companies prepare for the new rules?
Organisations should start by conducting detailed gap assessments of existing packaging lines, updating User Requirement Specifications and artwork, validating hardware like embossers and vision systems, retraining operators on new SOPs, and collaborating with experienced packaging compliance partners to avoid operational disruption and ensure readiness for inspections.




